
This page contains the mobility projects of InterSCity. Click on the “Page” link to see more details about each project.
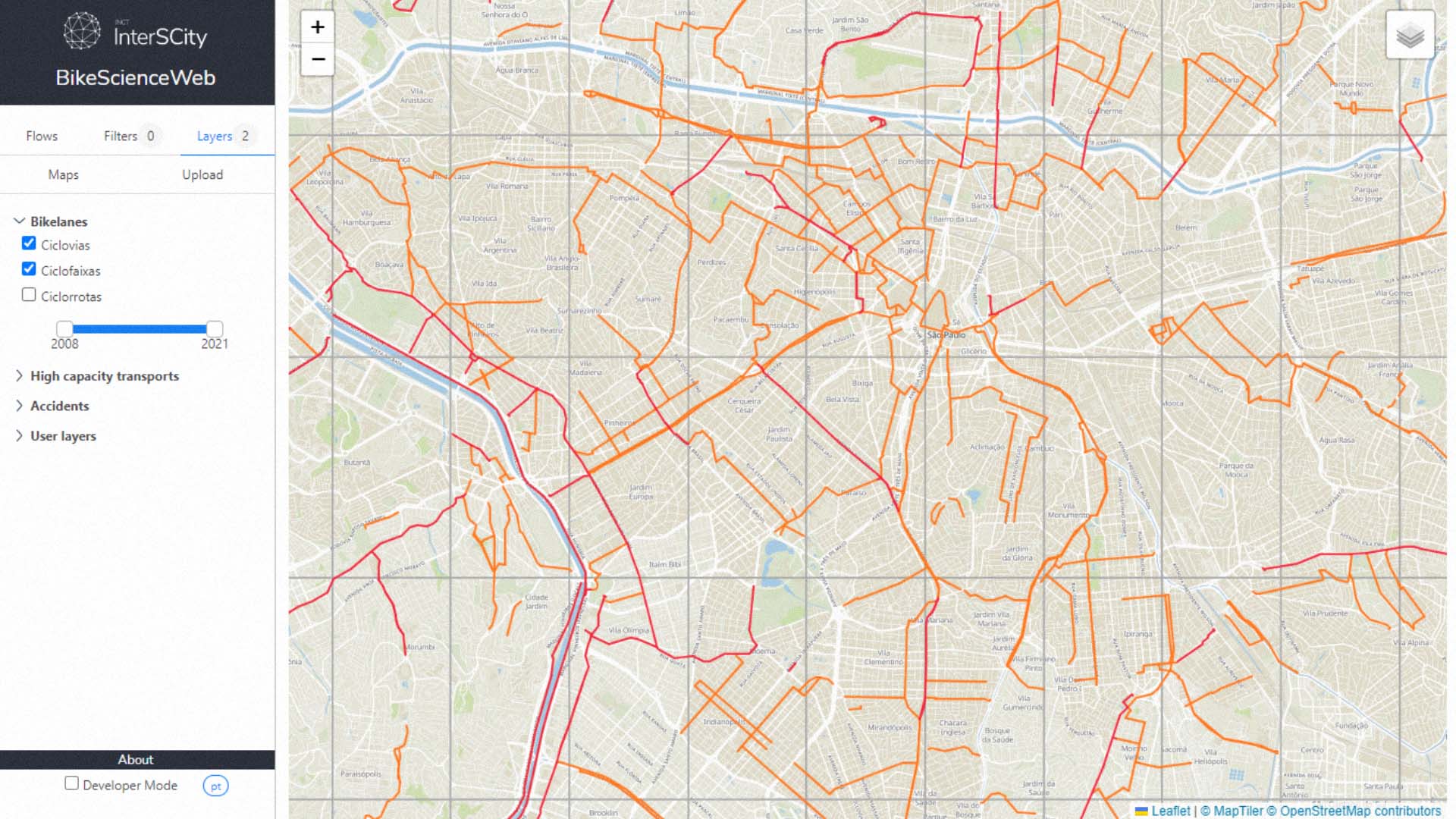
BikeScience is a Data Science tool that allows urban planners to analyze and understand the impact of urban bicycling in their cities. The tool uses data from Bike-Sharing Systems and travel surveys to analyze patterns of bike usage. Such knowledge can be used to support future planning and improvements regarding bicycling.
InterSCSimulator is an open-source, extensible, large-scale Traffic Simulator for Smart Cities developed in Erlang programming language, capable of simulating millions of agents using a real map of a large city. In the video below each color represents actors that are doing different actions such as going to work, going home or going to a hospital.
Abstract:
The excess of vehicles in metropolitan areas creates problems for first responders during an emergency response, delaying emergency vehicles at critical moments. One of the ways to reduce the effects of congestion on an emergency vehicle (EV) is to use preemption, i.e., changing the traffic lights’ phases along its route. This paper proposes an algorithm that uses the shock-wave principle to compute the time to dissipate a queue of vehicles ahead of the EV waiting at a traffic light and determine the appropriate timing to trigger the preemption of the traffic light. Extensive evaluations of the proposed algorithm simulating real scenarios of different cities and with varying levels of congestion show that, for the considered scenarios, it reduces up to 96.98% the loss time of the EV in traffic, resulting in better performances than the existing solutions.
► Monitoramento das metas de emissão dos contratos de transporte público:
► Análise detalhada das emissões do transporte público da cidade de São Paulo:
How data can keep the buses of Rio de Janeiro steadily flowing – Watch the Video.
Eletrificação do transporte público na COP 27 – Assista ao vídeo.
This study joins data from different sources to identify accessibility resources in the districts of the city of São Paulo. Ten databases were combined to analyze:
The goal is not to draw final conclusions, but to create a starting point for discussions. The model was put up from found resources, and it certainly presents several limiations. Therefore, other variables can and should be added to enrich the analysis.